| Programme annuel & rapport de suivi technique |
-

Rapport d'activités 2023
-

Programmes Techniques 2024
|
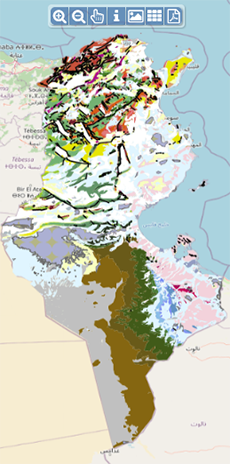
| Géocatalogue |
|
| Appels d'Offres |
-

ACQUISITION DES TICKETS RESTAURANT POUR LE PERSONNEL DE L’ONM
-

CHOIX D’UNE COMPAGNIE D’ASSURANCE
-

ACQUISITION ET MISE EN ŒUVRE D’UN PROGICIEL DE GESTION INTEGRE
|
|
Investir en Tunisie |


|
|
|
|
|
::
Documentation and Editions
>>
Research library
|
| |
|
[
Search by author
]
[
Search keyword
]
[
Search by index
]
[
Search by category
]
|
title of the reference :
|
Mercury degassing rate from mineralized areas in the Mediterranean basin.
|
|
Publication Date:
|
1997
|
|
Author :
|
Ferrara R., Maserti B.E., Andersson, Edner H., Ragnarson, Svanberg
|
|
Catalogue type :
|
Livre
|
|
Catalogue reference :
|
(NLD) Water Air Soil Pollut. Mercury degassing rate from mineralized areas in the Mediterranean basin. Knowledge of the natural emissions of mercury in the Mediterranean basin, which has large cinnabar anomalies, has particular weight as these deposits could be an important source of atmospheric mercury. Data on the degassing rate of mercury from soils sampled both in mineralized areas (Mt. Amiata, Italy and Almaden, Spain)and rural areas are reported. Measurements were carried out 'in situ' using a transparent flux chamber and collecting the gaseous mercury on gold collectors. The highest values were observed in Almaden over the roasted cinnabar banks (up to 100 mug/m**(2)h)from past and present mining activity. In Italian rural areas the values of the volatilization rate of mercury are on the order of few ng/m**(2)h. The degassing rate was observed to be strongly dependent on the ambient temperature and not only seasonal but also daily variations were measured in all the studied areas.
Anomalie ; Emission atmosphérique ; Sol ; Cinabre ; Volatilisation ; Mercure ; Dégazage ; Température ; Variation saisonnière ; Zone rurale ; Atmosphère ; Mine ; Variation temporelle ; Matière volatile ; Pollution ; Sulfure ; Italie : Espagne ; Turquie ; Slovénie ; Tunisie Ragnarson Svanberg Maserti B.E. Andersson Edner H. Ferrara R. Géothechniques, Géologie de l'ingénieur
|
|
Indexation decimale :
|
Géothechniques, Géologie de l'ingénieur
|
|
Keywords :
|
Anomalie ; Emission atmosphérique ; Sol ; Cinabre ; Volatilisation ; Mercure ; Dégazage ; Température ; Variation saisonnière ; Zone rurale ; Atmosphère ; Mine ; Variation temporelle ; Matière volatile ; Pollution ; Sulfure ; Italie : Espagne ; Turquie ; Slovénie ; Tunisie
|
|
Summary :
|
Knowledge of the natural emissions of mercury in the Mediterranean basin, which has large cinnabar anomalies, has particular weight as these deposits could be an important source of atmospheric mercury. Data on the degassing rate of mercury from soils sampled both in mineralized areas (Mt. Amiata, Italy and Almaden, Spain)and rural areas are reported. Measurements were carried out 'in situ' using a transparent flux chamber and collecting the gaseous mercury on gold collectors. The highest values were observed in Almaden over the roasted cinnabar banks (up to 100 mug/m**(2)h)from past and present mining activity. In Italian rural areas the values of the volatilization rate of mercury are on the order of few ng/m**(2)h. The degassing rate was observed to be strongly dependent on the ambient temperature and not only seasonal but also daily variations were measured in all the studied areas.
|
|
Exemplaries :
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



