| Programme annuel & rapport de suivi technique |
-

Rapport d'activités 2023
-

Programmes Techniques 2024
|
| Géocatalogue |
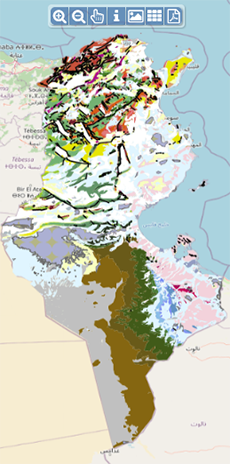
|
| Appels d'Offres |
-

ACQUISITION DES TICKETS RESTAURANT POUR LE PERSONNEL DE L’ONM
-

CHOIX D’UNE COMPAGNIE D’ASSURANCE
-

ACQUISITION ET MISE EN ŒUVRE D’UN PROGICIEL DE GESTION INTEGRE
|
|
Investir en Tunisie |


|
|
|
|
|
::
Documentation and Editions
>>
Research library
|
| |
|
[
Search by author
]
[
Search keyword
]
[
Search by index
]
[
Search by category
]
|
title of the reference :
|
Spring mounds in southern Tunisia.
|
|
Publication Date:
|
1987
|
|
Author :
|
Roberts C.R., Mitchell C.W.
|
|
Catalogue type :
|
Livre
|
|
Catalogue reference :
|
(GBR) Geol. Soc. - Spec. Publ. Spring mounds in southern Tunisia. Chotts Djerid and Fedjadj lie in the arid zone of southern Tunisia, and are chemically active, artesian environments which give rise not only to extensive emergent groundwater gypsum and salt deposits, but also to landforms of more complex architecture. In some geological situations belts of spring mounds up to 25 or 30 m high straddle former high-level late Pleistocene lake shorelines. Spring mounds are circular, gypsiferous or calcareous, volcano-like structures fed by point sources of artesian water rising from aquifers in the Contnental Intercalaire and Complexe Terminal aquifer series. Similar mounds have been indentified around playas in the USA, Australia, Egypt, Iraq and elsewhere.In some mounds a central well is occupied by a small pond with water conduits in the base, whilst others are dry and degraded. In these latter, water is only present at depth and wind erosion and redeposition are moulding the landforms. The morphology of spring mounds is determined by the balance between aquifer pressure head, output, chemical content, net evaporation, aeolian activity, and plant colonisation. Their stratigraphy comprises alternations of erystalline, wind-blown gypsiferous sand, wash and splash deposits, and organic lavers arranged in overlapping sequences which dip outwards from the water source. Such deposits offer a potentially sensitive index of environmental changes in the late Quaternary and Holocene. bibliogr. relief continent ; source ; gypse ; hydrochimie ; sédimentation chimique ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Sud Orientale ; Tunisie Sud Occidentale Mitchell C.W. Roberts C.R. Géomorphologie, Pédologie
|
|
Indexation decimale :
|
Géomorphologie, Pédologie
|
|
Keywords :
|
relief continent ; source ; gypse ; hydrochimie ; sédimentation chimique ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Sud Orientale ; Tunisie Sud Occidentale
|
|
Summary :
|
Chotts Djerid and Fedjadj lie in the arid zone of southern Tunisia, and are chemically active, artesian environments which give rise not only to extensive emergent groundwater gypsum and salt deposits, but also to landforms of more complex architecture. In some geological situations belts of spring mounds up to 25 or 30 m high straddle former high-level late Pleistocene lake shorelines. Spring mounds are circular, gypsiferous or calcareous, volcano-like structures fed by point sources of artesian water rising from aquifers in the Contnental Intercalaire and Complexe Terminal aquifer series. Similar mounds have been indentified around playas in the USA, Australia, Egypt, Iraq and elsewhere.In some mounds a central well is occupied by a small pond with water conduits in the base, whilst others are dry and degraded. In these latter, water is only present at depth and wind erosion and redeposition are moulding the landforms. The morphology of spring mounds is determined by the balance between aquifer pressure head, output, chemical content, net evaporation, aeolian activity, and plant colonisation. Their stratigraphy comprises alternations of erystalline, wind-blown gypsiferous sand, wash and splash deposits, and organic lavers arranged in overlapping sequences which dip outwards from the water source. Such deposits offer a potentially sensitive index of environmental changes in the late Quaternary and Holocene.
|
|
Exemplaries :
|
TU900
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



