| Programme annuel & rapport de suivi technique |
-

Programmes Techniques 2025
-

Rapport d'activités 2023
|
| Géocatalogue |
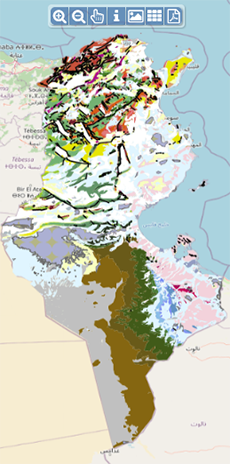
|
| Appels d'Offres |
-

DESIGNATION D’UN REVISEUR COMPTABLE POUR LES EXERCICES 2025-2026-2027
-

ACQUISITION DE MATERIEL INFORMATIQUE ET EQUIPEMENTS RESEAUX
|
|
Investir en Tunisie |


|
|
|
|
|
::
Documentation and Editions
>>
Research library
|
| |
|
[
Search by author
]
[
Search keyword
]
[
Search by index
]
[
Search by category
]
|
title of the reference :
|
Quantitative evaluation of the geologic evaluation and hydrocarbon potential of the Gulf of Gabes.
|
|
Publication Date:
|
1994
|
|
Author :
|
Yukler M.A., Moumen A., Daadouch I., Yukler M.A., Meskini A., Saidi Moncef, Jarraya Habib, Bouhlel H.
|
|
Catalogue type :
|
Livre
|
|
Catalogue reference :
|
Quantitative evaluation of the geologic evaluation and hydrocarbon potential of the Gulf of Gabes. A quantitative basin modelling study is carried out, using YUKLERPCr software and all the available data in ETAP, Tunis, to determine the geologic evolution and hydrocarbon potential of the Gulf of Gabes. Fifty-eight wells pressure, porosity, temperature and maturity data are modelled to construct the conceptual model in terms of paleoenvironments, lithofacies, type of geologic events and their durations, and heat flow. The conceptual model is then used in the modelling of fifty-one pseudo-wells. The computed subsidence and the optimized heat flow histories show that the subsidence of the subbasins within and around the Gulf of Gabes from the Callovian to the Berriasian, from the Aptian to the Paleocene and from the the Langhian to Resent were the result of tensional forces. The heat flow values first increased and then decreased during these times. The subsidence from the mid Paleocene to the Oligocene was not controlled by tensional forces. The optimized heat flow values were constant during this time and the seismic data show that the Eocene sediments are onlapping on to the underlying older formations. The subbasins were subjected to more then one compressional event from the Langhian to recent. Major upliff and erosion took place during the Tortonian and the mid-late Pliocene which altered the subsurface topography and affected the timing of trap formation and trap size. The last heat flow increase and the late Tertiary sedimentation were the controling factors for the generation and migration of hydrocarbons. The effective hydrocarbon generation and migration took place only during the last 4 my within and around the Gulf of Gabes.
offshore ; pétrole ; roche mère hydrocarbure ; densité ; modèle théorique ; lithofaciès ; paléogéographie ; subsidence ; Eocène ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Sud Orientale ; Golfe de Gabès Meskini A. Saidi Moncef Jarraya Habib Moumen A. Daadouch I. Yukler M.A. Yukler M.A. Bouhlel H. Gîtologie
|
|
Indexation decimale :
|
Gîtologie
|
|
Keywords :
|
offshore ; pétrole ; roche mère hydrocarbure ; densité ; modèle théorique ; lithofaciès ; paléogéographie ; subsidence ; Eocène ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Sud Orientale ; Golfe de Gabès
|
|
Summary :
|
A quantitative basin modelling study is carried out, using YUKLERPCr software and all the available data in ETAP, Tunis, to determine the geologic evolution and hydrocarbon potential of the Gulf of Gabes. Fifty-eight wells pressure, porosity, temperature and maturity data are modelled to construct the conceptual model in terms of paleoenvironments, lithofacies, type of geologic events and their durations, and heat flow. The conceptual model is then used in the modelling of fifty-one pseudo-wells. The computed subsidence and the optimized heat flow histories show that the subsidence of the subbasins within and around the Gulf of Gabes from the Callovian to the Berriasian, from the Aptian to the Paleocene and from the the Langhian to Resent were the result of tensional forces. The heat flow values first increased and then decreased during these times. The subsidence from the mid Paleocene to the Oligocene was not controlled by tensional forces. The optimized heat flow values were constant during this time and the seismic data show that the Eocene sediments are onlapping on to the underlying older formations. The subbasins were subjected to more then one compressional event from the Langhian to recent. Major upliff and erosion took place during the Tortonian and the mid-late Pliocene which altered the subsurface topography and affected the timing of trap formation and trap size. The last heat flow increase and the late Tertiary sedimentation were the controling factors for the generation and migration of hydrocarbons. The effective hydrocarbon generation and migration took place only during the last 4 my within and around the Gulf of Gabes.
|
|
Exemplaries :
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



