| Programme annuel & rapport de suivi technique |
-

Programmes Techniques 2025
-

Rapport d'activités 2023
|
| Géocatalogue |
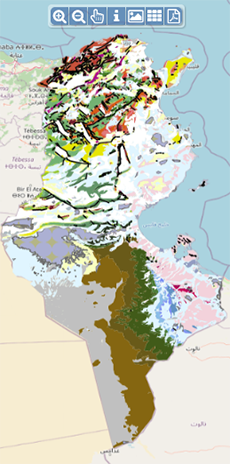
|
| Appels d'Offres |
-

DESIGNATION D’UN REVISEUR COMPTABLE POUR LES EXERCICES 2025-2026-2027
-

ACQUISITION DE MATERIEL INFORMATIQUE ET EQUIPEMENTS RESEAUX
|
|
Investir en Tunisie |


|
|
|
|
|
::
Documentation and Editions
>>
Research library
|
| |
|
[
Search by author
]
[
Search keyword
]
[
Search by index
]
[
Search by category
]
|
title of the reference :
|
Paleocene-Early Eocene Alkaline volcanic activity in Tunisia phosphatic sediments : comparison with Cretaceous magmatism and geodynamic signifiance.
|
|
Publication Date:
|
1998
|
|
Author :
|
Sassi Beji Aicha, Laridhi-Ouazaa Néjia, Zaier Ali, Clocchiatti Robert
|
|
Catalogue type :
|
Livre
|
|
Catalogue reference :
|
Paleocene-Early Eocene Alkaline volcanic activity in Tunisia phosphatic sediments : comparison with Cretaceous magmatism and geodynamic signifiance. Traces of Paleocene-Eocene volcanic activity have been discovered in phosphatic sediments and encountered in some peutroleum well. The glassy inclusions in ilmenite, apatite and quartz crystals from some phosphatic levels located East, South and North of the Kasserine paleo-island permit to evidence an essentially explosive volcanic activity during the Paleocene and Eocene stages. Glassy inclusions and host minerals compositions prove that a complete alkaline series evolved by a fractional crystallisation process from basaltic to trachytic and rhyolitic terms. In Aoudna 1 well the volcanic deposits consist mainly of pumice. This alkaline volcanism displays similar characteristics with the Cretaceous one and underlines a regional tectonic extensive phase, which favoured the ascent of magmas. The existence of a locally compressive zone allows its trapping into shallow chambers and its chemical evolution by fractionation. This environment characterised by a high geothermal gradient is favourable to organic matter maturation.
ETAP MEMOIR N°12
volcano sédimentaire ; phosphate ; magmatisme ; géodynamique ; inclusion minérale ; Paléogène ; Crétacé supérieur ; Yprésien ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Sud occidentale ; Tunisie Centrale ; Tunisie nord Occidentale ; Tunisie Orientale-Sahel Clocchiatti Robert Laridhi-Ouazaa Néjia Zaier Ali Sassi Beji Aicha Volcanisme + Métamorphisme
|
|
Indexation decimale :
|
Volcanisme + Métamorphisme
|
|
Keywords :
|
volcano sédimentaire ; phosphate ; magmatisme ; géodynamique ; inclusion minérale ; Paléogène ; Crétacé supérieur ; Yprésien ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Sud occidentale ; Tunisie Centrale ; Tunisie nord Occidentale ; Tunisie Orientale-Sahel
|
|
Summary :
|
Traces of Paleocene-Eocene volcanic activity have been discovered in phosphatic sediments and encountered in some peutroleum well. The glassy inclusions in ilmenite, apatite and quartz crystals from some phosphatic levels located East, South and North of the Kasserine paleo-island permit to evidence an essentially explosive volcanic activity during the Paleocene and Eocene stages. Glassy inclusions and host minerals compositions prove that a complete alkaline series evolved by a fractional crystallisation process from basaltic to trachytic and rhyolitic terms. In Aoudna 1 well the volcanic deposits consist mainly of pumice. This alkaline volcanism displays similar characteristics with the Cretaceous one and underlines a regional tectonic extensive phase, which favoured the ascent of magmas. The existence of a locally compressive zone allows its trapping into shallow chambers and its chemical evolution by fractionation. This environment characterised by a high geothermal gradient is favourable to organic matter maturation.
|
|
Exemplaries :
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



