| Annual program and technical progress report |
-

Activity Report 2024
-

Technical Program 2025
|
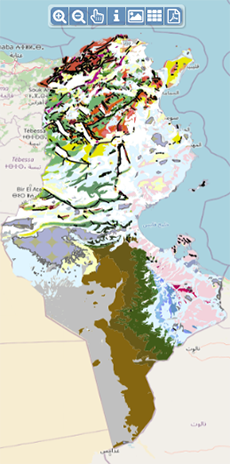
| Geocatalogue |
|
| Invitation to
tender |
-

Designation of a Lawyer or a Professional Law Firm to Represent the NOM
|
|
Invest in Tunisia |

|
|
|
|
|
::
Documentation and Editions
>>
Research library
|
| |
|
[
Search by author
]
[
Search keyword
]
[
Search by index
]
[
Search by category
]
|
title of the reference :
|
Iron and Manganese dynamics in the sediments of Ghar El Meleh Lagoon.
|
|
Publication Date:
|
2001
|
|
Author :
|
Added Ayed
|
|
Catalogue type :
|
Livre
|
|
Catalogue reference :
|
N°67 (TUN) Notes Serv. Géol. N°67 Iron and Manganese dynamics in the sediments of Ghar El Meleh Lagoon. Analyses of iron and manganese in the sediment of Ghar El Melh Lagoon showed the following results : Fe and Mn hydroxides and oxides and AVS concentrations exhibited in the same decrease in the 0-10 cm depth interval.The laboratory results showed that the maximum of Fe2+ and Mn 2+ liberation occured at a depth of 15-18 cm in the sediment where SO4 2- reduction revival was observed.These results suggest that iron and manganese reduction was coupled with sulfate reduction in the sediment.The laboratory results showed that production rates of Fe2+ and Mn2+ as well as reduction rates of SO42- exhibited a Gaussian from between 5 and 36 cm in the sediment. However, in the 0-5cm depth interval, SO42- reduction was high, while Mn2+ production was low and that of Fe2+ varied with time. Additionally, the laboratory study showed a similarity between the distribution of SiO2 and SO42- rates. Pore water distribution of Fe2+,Mn2+and SO42- seems to be affected by the bioirrigation and wind action.The high benthic fluxes of Mn2+ suggested that steep gradients of Mn2+ and probably Fe2+ existed at the sediment-water interface and this does mean that bacterial reduction of Mn and Fe oxides could occur at this zone. By modeling the pore water concentrations of Fe2+ and Mn2, rates of both bioirrigation and wind action were estimated to 10dm2 y-1 in summer and 100 dm2y-1 in spring at the 0-6 cm depth interval of sefdiments.
fer ; manganèse ; porosité ; interface ; sédiment lacustre ; corrélation ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Nord Orientale ; Gar El Melh Added Ayed Géochimie
|
|
Indexation decimale :
|
Géochimie
|
|
Keywords :
|
fer ; manganèse ; porosité ; interface ; sédiment lacustre ; corrélation ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Nord Orientale ; Gar El Melh
|
|
Summary :
|
Analyses of iron and manganese in the sediment of Ghar El Melh Lagoon showed the following results : Fe and Mn hydroxides and oxides and AVS concentrations exhibited in the same decrease in the 0-10 cm depth interval.The laboratory results showed that the maximum of Fe2+ and Mn 2+ liberation occured at a depth of 15-18 cm in the sediment where SO4 2- reduction revival was observed.These results suggest that iron and manganese reduction was coupled with sulfate reduction in the sediment.The laboratory results showed that production rates of Fe2+ and Mn2+ as well as reduction rates of SO42- exhibited a Gaussian from between 5 and 36 cm in the sediment. However, in the 0-5cm depth interval, SO42- reduction was high, while Mn2+ production was low and that of Fe2+ varied with time. Additionally, the laboratory study showed a similarity between the distribution of SiO2 and SO42- rates. Pore water distribution of Fe2+,Mn2+and SO42- seems to be affected by the bioirrigation and wind action.The high benthic fluxes of Mn2+ suggested that steep gradients of Mn2+ and probably Fe2+ existed at the sediment-water interface and this does mean that bacterial reduction of Mn and Fe oxides could occur at this zone. By modeling the pore water concentrations of Fe2+ and Mn2, rates of both bioirrigation and wind action were estimated to 10dm2 y-1 in summer and 100 dm2y-1 in spring at the 0-6 cm depth interval of sefdiments.
|
|
Exemplaries :
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



