| Annual program and technical progress report |
-

Technical Program 2025
-

Activity Report 2023
|
| Geocatalogue |
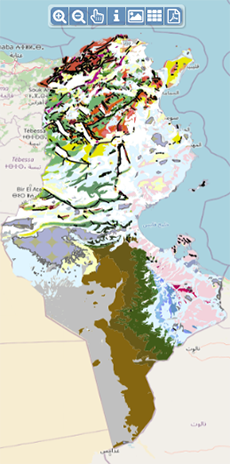
|
| Invitation to
tender |
-

REALIZATION OF THE TRAINING PLAN FOR THE YEAR 2022
-

ACQUISITION OF TWO SERVICE CARS
-

ACQUISITION OF GEORADAR EQUIPMENT AND ITS ACCESSORIES
|
|
Invest in Tunisia |

|
|
|
|
|
::
Documentation and Editions
>>
Research library
|
| |
|
[
Search by author
]
[
Search keyword
]
[
Search by index
]
[
Search by category
]
|
title of the reference :
|
Geological and Geochemical study of Pb-Zn, F and Ba ores in Zaghouan province Northeasten Tunis.
|
|
Publication Date:
|
1997
|
|
Author :
|
Souissi Foued, Sassi Radhia
|
|
Catalogue type :
|
Livre
|
|
Catalogue reference :
|
Geological and Geochemical study of Pb-Zn, F and Ba ores in Zaghouan province Northeasten Tunis. first Mining Conf in the Great Jamahiriya Zaghouan province located northeastern Tunis is Characterized as contaning Pb, Zn, F, Ba and Sr deposits. The geology of the study area consists of thick Jurassic (lower Lias)Formation and Ressas Formation (Kimmeridgian-Tithonian-Berriasian)respectively. These formations are characterized particulary at their upper portions by dolomitization, silicification, erosion, and non-deposition. They are overlaid by thin phosphatic beds belonging to Middle Lias or Upper Cretaceous. Tne ores are located along non-conformity surfaces as lenses or accumulations (j. el satah, j. kohol, Hammam Zriba)where their depositions took place. Furthermore, these deposits are also found as veins or in faults (j. Oust and j. Ressas)or with tectonic breccia (H. Jedidi)or within Karst voids with faults (Sidi Taya). These deposits consist of fluorite within galena, sphalarite and barium and stronium sulfates. Furthermore geochemical analysis of host rocks showed that the concentration of major elements in these deposits does not exceed their average concentrations in carbonate rocks. Microthermometry analysis of fluid inclusions in fluorine and quartz showes that these ores were deposit due to the action of hydrothermal solutions that had a temperature from 100-250°C and salinity from 132 to 34 NaCl equivalent, morover, most samples contain oil inclusions. Geochemichal analysis of fluid inclusions in fluorite contain high percentage of Na+, K+, Ca++, Mg++, Cl- and SO4-. Hence all these geological and geochemical and physiochemical studies led to the conclusion that these ores were deposited due to a lowering of pressure and temperature of hydrothermal solutions through their descend as well the activity of Ca++ ions resulted from carbonate dissolution througn which these solutions were descended. résumé plomb ; zinc ; fluorite ; barite ; analyse ; microthermométrie ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Nord Orientale ; Zaghouan ; j. Oust ; j. Ressas ; Hammam Jedidi ; Sidi Taya Sassi Radhia Souissi Foued Gîtologie
|
|
Indexation decimale :
|
Gîtologie
|
|
Keywords :
|
plomb ; zinc ; fluorite ; barite ; analyse ; microthermométrie ; Tunisie ; Tunisie Nord Orientale ; Zaghouan ; j. Oust ; j. Ressas ; Hammam Jedidi ; Sidi Taya
|
|
Summary :
|
Zaghouan province located northeastern Tunis is Characterized as contaning Pb, Zn, F, Ba and Sr deposits. The geology of the study area consists of thick Jurassic (lower Lias)Formation and Ressas Formation (Kimmeridgian-Tithonian-Berriasian)respectively. These formations are characterized particulary at their upper portions by dolomitization, silicification, erosion, and non-deposition. They are overlaid by thin phosphatic beds belonging to Middle Lias or Upper Cretaceous. Tne ores are located along non-conformity surfaces as lenses or accumulations (j. el satah, j. kohol, Hammam Zriba)where their depositions took place. Furthermore, these deposits are also found as veins or in faults (j. Oust and j. Ressas)or with tectonic breccia (H. Jedidi)or within Karst voids with faults (Sidi Taya). These deposits consist of fluorite within galena, sphalarite and barium and stronium sulfates. Furthermore geochemical analysis of host rocks showed that the concentration of major elements in these deposits does not exceed their average concentrations in carbonate rocks. Microthermometry analysis of fluid inclusions in fluorine and quartz showes that these ores were deposit due to the action of hydrothermal solutions that had a temperature from 100-250°C and salinity from 132 to 34 NaCl equivalent, morover, most samples contain oil inclusions. Geochemichal analysis of fluid inclusions in fluorite contain high percentage of Na+, K+, Ca++, Mg++, Cl- and SO4-. Hence all these geological and geochemical and physiochemical studies led to the conclusion that these ores were deposited due to a lowering of pressure and temperature of hydrothermal solutions through their descend as well the activity of Ca++ ions resulted from carbonate dissolution througn which these solutions were descended.
|
|
Exemplaries :
|
TU1994
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



